This post will explain nameserver. “Nameserver” is a term you’ve most likely seen thrown around in your time as a site owner, whether you’re establishing a new domain or configuring your servers. A lot of individuals would see that term, shrug, and be fine with never knowing what it implies. But you’re here, so we suspect you’re 1 of those people. You’re curious.
What Is a Nameserver? & Why Does It Matter?
In this article, you can know about nameserver here are the details below;
Nameservers aren’t exactly a public-facing innovation, however they’re vital to the success of your site and any site that uses the domain system. Without nameservers, we could not use domain to access our favorite sites, making the internet much less functional (and fun).
In this guide, we’ll go over the essential things to learn about nameservers and your website– what they actually do, how they suit your visitors’ experience, and how you can set them approximately serve your site. Let’s get going.
What is a nameserver?
To comprehend what nameservers are and the role they play, let’s review what occurs when you visit a website through a browser. Also check Call transcription
Every device linked to the internet, from PCs to mobile phones to servers, has its own IP address. An IP address is an unique sequence of four numbers that recognizes the device to other gadgets. For instance. The reality is a little bit more intricate than this, but we’ll keep things basic for today.).
When you go to a site, your web internet browser sends out a demand to the IP address of the webserver that you offer. Except, of course, you don’t give the internet browser the IP address of the webserver yourself. Think of needing to memorize an unique IP address for every site you wish to go to– that would be a headache, or we ‘d all need fantastic memories.
Instead, you simply supply the domain of the website you wish to reach. Rather of plugging 104.19.154.83 into your browser bar.
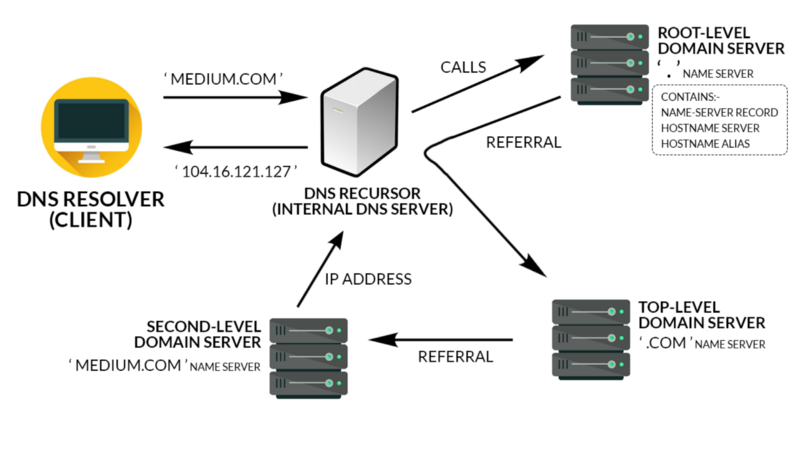
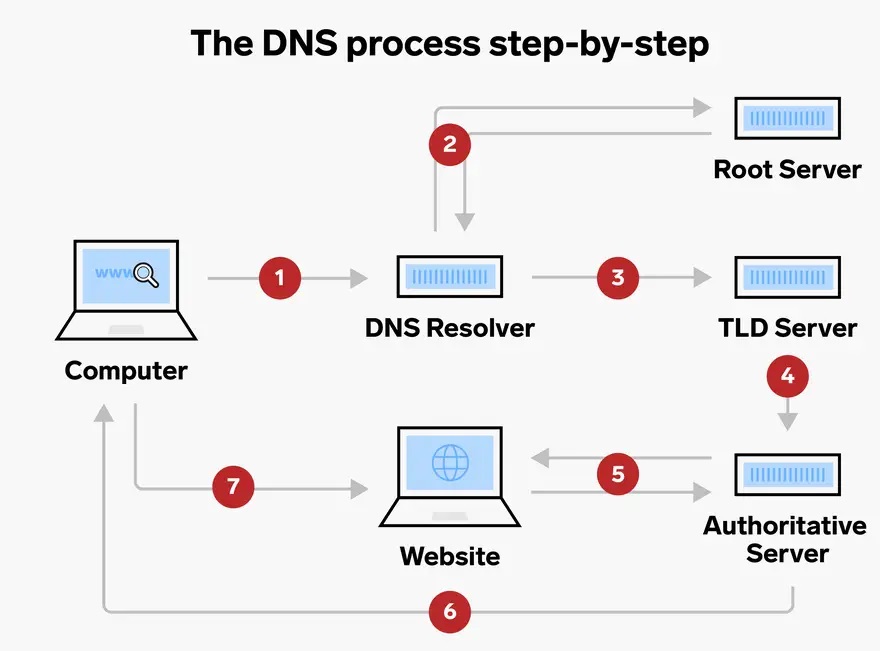
The Domain Name System, and DNS, is what allows us to utilize these alphabetic domain in place of IP addresses. The DNS is an international network of servers responsible for matching domain names to IP addresses, and it includes many types of devices. One of these makers is called a nameserver.
A nameserver is an server in the DNS that cracks domain into IP addresses. Nameservers supply & organize DNS records, separately of which sets a domain with several IP addresses. These servers act as the bridge in between domain names, which we people can keep in mind, with IP addresses, which computer systems can process.
So, any time you get in a domain name into your internet browser bar, the DNS first finds the nameserver accountable for that field name. The nameserver then fields your demand and finds the associated DNS record in its database. Once it discovers the record, the nameserver returns the IP address to your internet browser. Finally, your internet browser utilizes this brand-new IP address to ping the target webserver, and this webserver returns the websites you asked for.
We can consider a nameserver like a telephone directory– an out-of-date analogy, but it works. Say you (the web browser) wish to call your good friend, however you don’t have their number, just their name. First, you discover the telephone directory for the area this person lives (finding the best nameserver). Then, you explore the names to find your pal’s (finding the coordinating domain name). You see a telephone number (IP address) connected with their name. Now, you can call this number and talk to your pal (visit the site).
That’s a great deal of steps for what takes place in simply seconds or less. The entire process is rather fast, and even faster once you check out a website a second time. After very first going to a site once, your browser caches the domain’s associated IP address (like a small DNS record) so that, next time, your web browser can pull the DNS details from your local cache instead of calling the nameserver again. Also check Creative writing tools online
How are nameservers utilized?
As a site administrator, you’ve most likely seen the term “nameserver” used when purchasing a domain or web hosting.
When your domain registrar or hosting provider describes “nameservers,” they’re referring to the nameserver address used to locate the nameserver itself. Nameserver addresses appear like domain, except they do not bring us to sites. Rather, they get us to the nameservers that supply us with the IP address we desire.
When producing a website, you set up these nameserver addresses to point your domain name to the server that hosts your website. Most popular hosting suppliers make this very easy to do as part of the setup procedure. There’s no limitation to the variety of nameservers a site can have, but the majority of utilize two: one as the main nameserver and another as the fallback in case the very first nameserver stops working.
How to Set Up a Nameserver.
The majority of people purchase and register domain through a domain registrar. When your domain is signed up, it will most likely be located in the registrar’s own nameservers by bankruptcy.
You can keep it this way & write your DNS record to point your domain name to your webserver’s IP address. Or, you can choose to save your DNS record on a nameserver owned by your hosting company. This latter method is normally preferred, as you can manage your webserver and nameserver under one account.
There’s also the choice to utilize different nameservers through a material delivery network like Amazon CloudFront or Cloudflare that can improve overall website performance and security.
Whichever nameservers you select for your site, setting them up and customizing your DNS record to indicate your webserver is usually pretty simple. It will not involve any low-level setup, most likely just copying and pasting addresses. Keep in mind that changes to DNS records take up to 72 hours to upgrade internationally.
What is my nameserver?
Want to see out what nameservers your site (or any website) utilizes? It’s simple using an online lookup tool, as this info is publicly offered on the WHOIS procedure. Also check Social listening tools
Nameservers: Connecting Domains to IP Addresses.
Many internet users don’t know what nameservers are, and they don’t need to. However, these servers are crucial to how the web works today. Without them, we ‘d have to keep note of every IP address for every website we wished to go to. That does not seem like enjoyable for anyone.
Even if you’re a casual site owner, it helps to understand the function of nameservers and their role in the bigger DNS. That way, if something breaks on your website with regards to your domain, or if you are working several domains that all point to the very same IP address, you can discover your method around just a bit better.